Liability: Definition, Types, and Examples

Expenses are recorded on the income statement, directly affecting net income and, subsequently, retained earnings on the balance sheet. Misclassifying expenses or liabilities can distort a company’s financial health, affecting investor confidence and decision-making. Non-current liabilities are long-term obligations that extend beyond a year, such as bonds payable or long-term leases. On a balance sheet, liabilities show a company’s financial obligations to its lenders and creditors due to past transactions.
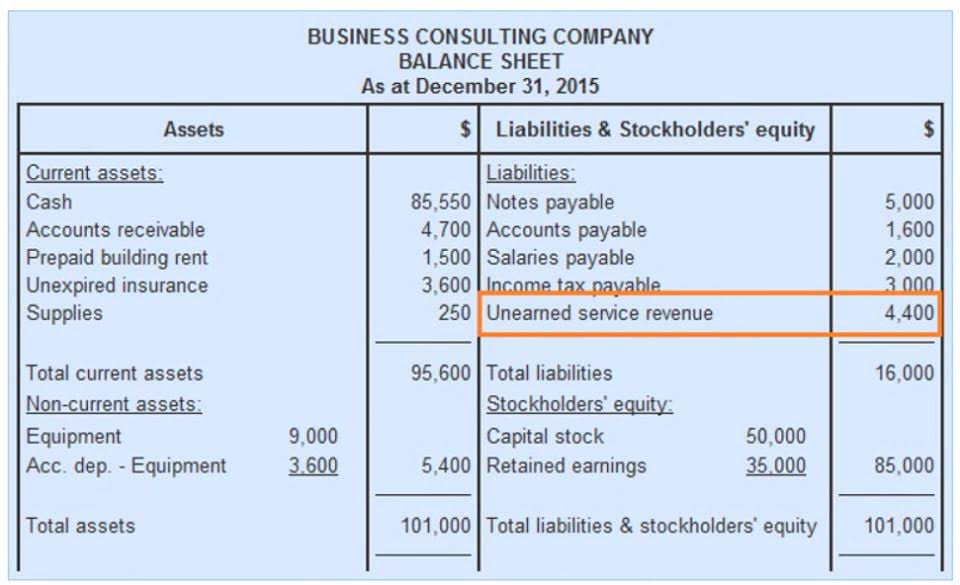
Overview: Difference between assets and liabilities
A long-term liability supported by what is liability in accounting a mortgage is a secured debt. An unsecured debt is one for which the creditor relies primarily on the integrity and general power of the borrower. The gap between the two methods of valuation is significant as regards long term liabilities.
- The terms owners’ equity, proprietorship, capital and net worth are used interchangeably.
- Wages PayableWages payable is the total amount owed to employees for services already rendered but not yet paid.
- A “medium probability” contingency is one that satisfies either, but not both, of the parameters of a high probability contingency.
- They are recorded on a company’s balance sheet under the liabilities section, alongside assets and equity.
- Only record a contingent liability if it is probable that the liability will occur, and if you can reasonably estimate its amount.
Types of Liabilities
- Differences exist in accounting for the owners’ equity among a sole proprietorship, partnership and company form of organisation.
- Here are a few quick summaries to answer some of the frequently asked questions about liabilities in accounting.
- They include debts or obligations you owe to others, often seen on your balance sheet.
- The opinions of analysts are divided in relation to modeling contingent liabilities.
By keeping a clear understanding of their obligations and managing them effectively, businesses can maintain long-term financial success. Many accounting firms also deal with the current portion of long-term debt – that slice of a larger loan that’s due within the next 12 months. These obligations typically get paid using your current assets like cash or by creating new current liabilities.
What is a Contingent Liability?
This knowledge helps to assess a company’s financial health, evaluate its ability to meet its obligations, and make informed decisions about investments and financing. Understanding liabilities is essential for businesses since they provide necessary financing, facilitate transactions, and impact financial performance. Liabilities help How to Run Payroll for Restaurants companies manage cash flow and invest in new projects while maintaining a strong balance sheet.


Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due one year or longer after the end of the period. Since the time value of money can be large, long-term liabilities are often valued at their present value, where current liabilities are at nominal value. A liability represents a probable future sacrifice of economic benefits, stemming from present obligations due to past transactions. These obligations require the future transfer of assets or provision of services. In a sense, a liability is a creditor’s claim on https://grupascout.pl/2022/08/25/instructions-for-form-3115-12-2022-internal/ a company’ assets.

What is a Deferred Liability?
Receipt of proceeds may be evidence that an enterprise has incurred one or more liabilities, but it is not conclusive evidence. According to Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, liability is “the financial obligation of an enterprise other than owners’ funds”. The existence of a past transaction is an important element in the definition of liabilities.


